Unveiling Japan’s Sustainable Practices

Japan has a rigorous recycling system in place to enforce recycling at a household level. Owing to the efforts made to embrace sustainable practices, Japan has ranked high in the sustainability index. This article aims to explore Japan’s unique approach to recycling, influenced by cultural values, government policies, and innovations, while also comparing this to the recycling practices found in other European countries, and how these different practices can affect international businesses operating in Japan.
Japan’s traditional approach to recycling
The concept of reusing and recycling is deep rooted in various aspects of Japanese society. The term “MOTTAINAI” gained international recognition as it was referenced by various environmentalists worldwide. The concept of “MOTTAINAI” essentially means “how wasteful”, discouraging any practices that deem wasteful. Whether this is throwing out perfectly consumable or usable products or replacing products before they are worn out, “MOTTAINAI” can be used in various ways throughout most people’s livelihood. This concept also extends beyond mere material waste and encourages gratitude for what one has and a sense of responsibility towards future generations.
Rooting from “MOTTAINAI”, at the heart of Japan’s recycling initiatives is the “3Rs” framework: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle. Recently this 3Rs framework has expanded to 4Rs. In many western contexts 4Rs is Reduce, Reuse, Recycle and Recover, however, in Japan 4Rs refers to the usual 3Rs and adds Refuse. 4R in Japan aims to advocate for people to refuse single use plastic, and other environmentally harmful products, or to refuse any act that may be harmful to the environment.
Building on Japan’s traditional mindset of “MOTTAINAI” and implementing the 4R/3R strategy, reusing and recycling habits have been a large part of many Japanese livelihoods.

Rules and regulations regarding recycling
Many European countries excel in waste management and recycling. Countries such as the Netherlands offer separate bins so residents can separate their waste accordingly. Largely, these bins are separated into the following categories; paper, plastic, glass and general waste. A similar scene can be seen in the UK as well.
While Japan follows a similar recycling method, it seems that Japan’s waste management takes it to another level. These guidelines are managed at a municipality level and differ significantly depending on where you reside. In most cities and towns, waste is meticulously sorted into categories such as combustible, non-combustible, recyclable, and bulky waste. Residents are required to follow strict guidelines for waste disposal, including using designated garbage bags and adhering to specific collection days.
Below you can see Shinjuku city, one of Japan’s populated city’s 2024 guidelines of waste disposal.

Even amongst recyclable waste, each item needs to be collected in a different manner. For example, paper waste must be piled and tied as shown in the image below. Plastic waste is separated into waste that only contains plastic, mixed waste of plastic and other materials and plastic bottles. Size and cleanliness of the waste are also taken into consideration and have different ways to dispose of the waste.

Case Study: Innovative Recycling
Tokyoesque has conducted multiple research on Japanese consumer’s attitude and perception towards recycling. While this continues to change, Japanese consumers are increasingly becoming more conscious about recycling and environmentally friendly packaging and labels that indicate clear ways to recycle are now crucial. Below are some of the examples large companies are doing to initiate recycling in Japan.
In 2011, Suntory established a B to B mechanical recycling system in collaboration with Kyoei Sangyo Co., pioneering the use of recycled PET resin for new bottles. By 2030, Suntory aims for all PET bottles to use recycled and plant-derived materials exclusively. However, despite these sustainable initiatives, they are not prominently featured on product labels.
In 2019, Kit Kat in Japan made a significant shift from plastic to paper packaging, a move expected to reduce plastic usage by about 450 tonnes annually. This transition came with a unique approach, where after consumers are done eating the chocolate, they can craft the packaging into origami cranes or write small messages to each other. Numerous photos of origami cranes made from KitKat packages have circulated on social media, effectively showcasing the brand’s commitment to environmental responsibility.
Furthermore, Japan’s recycling efforts are supported by advanced technology and infrastructure. Recycling facilities across the country utilize state-of-the-art equipment and processes to sort and process materials efficiently. This technological innovation not only enhances the effectiveness of recycling initiatives but also minimizes environmental impact by reducing energy consumption and emissions.
Mitsubishi Electric’s pioneering recycling technology harnesses the power of static electricity for efficient sorting of plastics based on their electrostatic properties. This innovative approach not only optimizes the recycling process, but also enhances its effectiveness. With plans to commercialize this technology by fiscal year 2024, Mitsubishi Electric aims to extend its impact beyond electronics recycling to cater to various industries. By eliminating the need for manual sorting, this advancement promises to significantly improve recycling rates and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Similarly, Ebara Corporation is driving progress in chemical recycling, focusing on the extraction of gas components from mixed waste for plastic regeneration. This forward-thinking approach holds immense potential for transforming plastic waste into valuable resources. With a target for practical application by 2030, Ebara Corporation’s technology represents a crucial step towards achieving a circular economy and reducing reliance on virgin plastics. By converting waste into high-quality recycled materials, this innovation aligns with the growing global demand for sustainable solutions.
Japan is approaching recycling methods through various lenses, from a practical perspective of waste management to using sustainable materials for their products to cultural perspectives where they incorporate small traditional practices as using their wrappers as origami or small letters and of course, the innovative ways as developing new technology for better waste separation which contributes to a more sustainable tomorrow.

Recycling in Japan: Messages you need to convey
As Japan houses some of the more confusing recycling processes, Japanese companies have aimed to make this easier by labeling their products with the right icon and marks to make disposing of these waste easier. Some of these icons are displayed below.
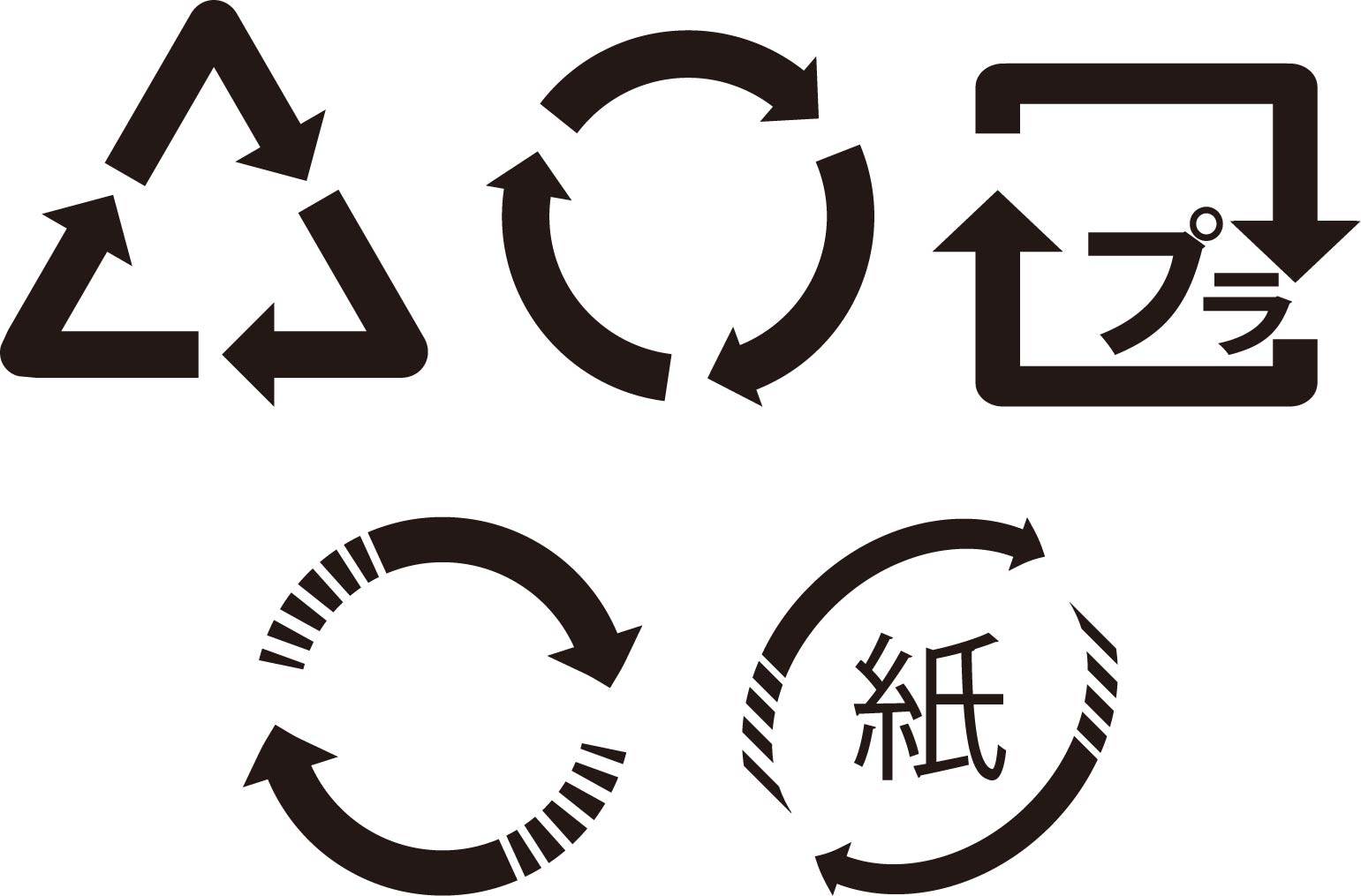
Foreign businesses have a need to adapt their products to align with Japan’s recycling standards and consumer preferences. This involves not only ensuring that products are designed with recyclability in mind but also understanding the nuances of Japan’s recycling system. For example, businesses can explore using packaging materials that are commonly accepted in Japan’s recycling infrastructure, such as PET bottles or cardboard packaging. Additionally, they can incorporate the above symbols and labels that clearly communicate the recyclability of their products to Japanese consumers, enhancing transparency and trust. By catering to the specific needs and expectations of the Japanese market, businesses can create a competitive advantage and strengthen their brand image as environmentally responsible entities.
Conclusion
Japan’s unique recycling efforts are a testament to its commitment to sustainability. Through advanced waste separation techniques, innovative initiatives, and cultural values that prioritize environmental conservation, Japan’s effort to sustainability starts at the household level. While much more initiatives to conserve the environment must be taken, Japan is seeing more environmentally friendly initiatives and this is becoming a standard practice for the Japanese consumers. Understanding Japan’s distinct recycling practices and utilising its advanced infrastructure can lead to new growth opportunities for businesses while making meaningful contributions to global sustainability goals. By integrating recycling icons to guide consumers or adding features that encourage upcycling, foreign brands can better align with Japanese consumer behavior and sustainability values.
At Tokyoesque, we support companies in navigating Japanese culture and consumerism. We help businesses not only understand Japan’s unique sustainability approach but also strategically position themselves to achieve their company goals within this market. By aligning with Japan’s eco-conscious values, companies can elevate their brand presence and drive success in this dynamic market.







